Digital signatures provide an easy and secure way to ensure the integrity and authenticity of digital documents. Whether you want to sign a business agreement or transmit important legal paperwork, using a digital signature is a process that offers the utmost security and compliance. But what exactly is a digital signature and how does it work?
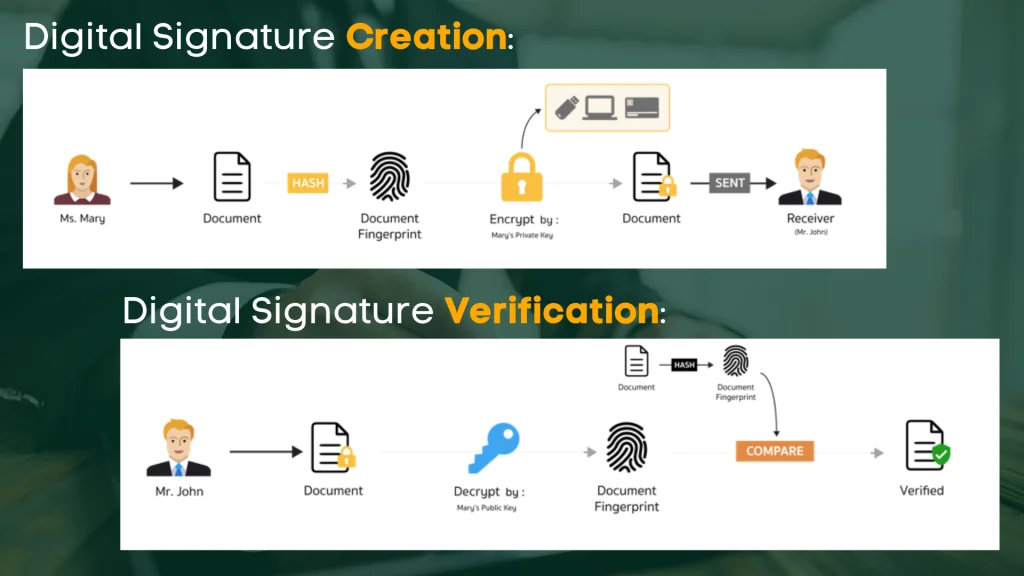
A digital signature is a unique electronic mark that is associated with a specified sender. It acts as a means of verifying the authenticity and integrity of a document. In order to create a digital signature, the sender must possess a certificate from a trusted authority. This certificate is issued by a Certificate Authority (CA) such as DocuSign, ensuring that the signature is compliant with the required standards-based processes.
So, how does it all work? When a sender wants to sign a document digitally, they use a software-based program that generates a pair of keys, known as the Public Key Infrastructure (PKI). These keys relate to each other in such a way that one belongs to the sender, while the other is kept privately by the recipient. By using their private key, the sender can sign the document and transmit it to the recipient.
But what if something goes wrong? Well, the recipient can verify the integrity and authenticity of the documents by using the sender’s public key. This ensures that the document has not been tampered with while transmitting and that it was indeed signed by the correct sender. By using digital signatures, organizations can enforce legally binding eSignatures without any worries about malicious tampering.
One of the most widely known digital signature platforms is DocuSign. As a qualified authority in the digital signing industry, DocuSign offers advanced features and processes for businesses to meet the legal requirements of document signing. With DocuSign’s services, users can create and sign legally binding documents, ensuring that the entire process is compliant and secure.
- Guide to digital signatures
- What do you want to do
- Why should you use PKI or PGP with digital signatures
- How do I create a digital signature
- What is Public Key Infrastructure PKI
- What is a Certificate Authority (CA)
- Why would I use a digital signature
- What digital signature solutions does DocuSign offer
- Are eSignatures based on digital signature technology legally enforceable
- What is a digital certificate
- What is the difference between Advanced Electronic Signature and Qualified Electronic Signature
- How do digital signatures work
- What is Public Key Infrastructure (PKI)
- What is a Certificate Authority CA
- What is a digital certificate
- Video:
- The TRUTH about Learning How to Code in 2024
Guide to digital signatures
In today’s digitally connected world, the need for secure and verified transactions is of utmost importance. This is where digital signatures come into play. A digital signature is a certificate-based process that allows for the validation and authentication of electronic documents or messages.
To understand how digital signatures work, it is essential to know the key components associated with them. The first component is a Certificate Authority (CA), which is a trusted third-party entity that issues digital certificates. These certificates contain information about the sender’s identity and are used to create a unique digital signature.
When a user wants to send a digitally signed document, they apply their private key to it, which is stored securely on their device. The document is then encrypted with the user’s public key. The digital signature ensures the integrity of the document during transmission and verifies the authenticity of the sender.
One of the main advantages of digital signatures is their legally enforceable nature. The process of verifying a digital signature involves validation against specific standards-based algorithms, which reduces the risk of tampering or forging. Unlike other eSignatures, such as those used in PGP, a digital signature is not only based on trust but also on the security of the entire Public Key Infrastructure (PKI).
In industries where everything from commerce to transmitting sensitive information occurs, digital signatures offer a reliable and secure way to ensure the authenticity of documents. With a digital signature, the recipient can trust that the document belongs to the specified sender and that it has not been altered during transmission.
Digital signatures are widely used in various fields, such as finance, healthcare, and legal sectors. They meet the highest standards of security and are legally binding. Electronic documents signed with a digital signature hold the same weight as traditional paper-based documents.
So, why should you consider using a digital signature? The main difference between a digital signature and an electronically signed document is the level of security and validation they provide. A digitally signed document offers a higher level of assurance and requires the recipient or relying party to have trust in the associated CA.
When sending or receiving a digitally signed document, it is important to be aware of the security measures in place. Malicious individuals may attempt to impersonate the sender or tamper with the document. By using a digital signature, you can be confident that the document has passed validation and is trustworthy.
In summary, digital signatures are an essential part of today’s digital world. They provide a secure and verifiable method for transmitting electronically signed documents. By incorporating a digital signature, you can ensure the integrity and authenticity of your documents, reducing the risk of fraud and ensuring compliance with legal and industry standards.
What do you want to do
A digital signature is a widely established part of doing business in the digital world. It relates to the process of transmitting and authenticating documents electronically, ensuring the required solutions for both the user and the business. Digital signatures have been associated with Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) and Certification Authorities (CA) to provide a trusted means of verifying the integrity and authenticity of documents.
So, what do you want to do with a digital signature?
If you are a user who needs to sign and send important documents electronically, digital signatures are the way to go. By using a digital signature, you can reduce the need for paper-based transactions and securely sign and transmit documents online. This not only saves time but also ensures the validity and integrity of the entire document transmission process.
For businesses, digital signatures act as a trusted authority for sending and receiving important documents. They are regulated and known to provide valid and trusted signatures, especially in industries where eSignatures are qualified and legally binding. Companies like Docusign and PGP have established themselves as advanced solutions for digitally signing documents.
But why use a digital signature? Digital signatures provide security by ensuring the integrity and authenticity of documents. They verify the identity of the signer and protect against tampering or malicious software. By using a digital signature, you can easily sign specified documents without the need for physical presence or the risk of document forgery.
So, if you want to ensure the security and integrity of your documents, a digital signature is what you need. It establishes a trusted connection between the sender and receiver, providing a secure means of transmitting and authenticating documents in the digital world.
Why should you use PKI or PGP with digital signatures
When it comes to digital signatures, using Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) or Pretty Good Privacy (PGP) can be an important part of ensuring the security and integrity of your signed documents.
Both PKI and PGP offer a means to create unique signatures that can be used to verify the identity of the signer and the authenticity of the document. These signatures are created by signing the document with a private key that belongs to the signer, and can be verified using the corresponding public key.
Using PKI or PGP for digital signatures offers several advantages:
Security and Integrity: PKI and PGP both provide a high level of security and integrity. The use of private and public key pairs ensures that only the signer can create a valid signature, and the signature itself acts as proof that the document has not been tampered with during transmission.
Compliance: PKI and PGP are widely accepted and regulated in industries and organizations that require legally enforceable signatures. By using PKI or PGP, you can meet the compliance requirements and ensure that your signed documents are legally valid.
Trust: PKI and PGP come with a built-in trust factor. Certificates are issued by trusted Certification Authorities (CAs) that verify the identity of the signer before issuing the certificate. This means that when someone receives a document with a PKI or PGP signature, they can be confident that the signature is valid and belongs to the named signer.
Open Standards: Both PKI and PGP are based on open standards, which means that they can be used with a wide range of software and solutions. This makes it easier for users to sign and verify documents without being tied to any specific software or vendor.
Revocation: PKI and PGP provide a mechanism for revoking certificates in case a private key is compromised or the signer’s identity is no longer valid. This ensures that even if a signature has been passed, the corresponding certificate can be revoked to prevent further use.
In conclusion, using PKI or PGP with digital signatures offers a secure and efficient way to sign and transmit electronic documents. It provides the highest level of security and integrity, meets compliance requirements, and offers trust and enforceability in the digital world.
How do I create a digital signature
If you want to sign documents electronically, or transmit them securely over the internet, you may want to create a digital signature. Digital signatures are widely used in industries such as finance, healthcare, and e-commerce to establish the authenticity and integrity of electronic documents.
But how does one create a digital signature? Well, the process is quite straightforward. First, you need to have a digital certificate issued by a trusted Certificate Authority (CA). This certificate is based on the widely accepted Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) and serves as proof of your identity in the digital world.
Once you have a digital certificate, you can use it to sign documents electronically. Most digital signature solutions offer software-based solutions that comply with industry-standard regulations. These solutions ensure that your digital signatures meet the legally specified requirements and are valid and verifiable.
When you create a digital signature, you are essentially applying a unique electronic mark to the document. This mark is generated using a key pair: a private key that only you possess and a public key that is openly available. The private key is used to sign the document, while the public key is used to verify the signature.
Creating a digital signature not only reduces the time and effort required to sign and transmit documents, but it also increases security. Digital signatures ensure that the document has not been tampered with or modified after it was signed, and they also provide a way to establish the authenticity of the signer.
So, why would you want to create a digital signature? The answer is simple: it allows you to sign documents digitally without the need for physical signatures. This opens up new possibilities for businesses as they can now sign and validate documents remotely, saving both time and resources.
Here’s how the process of creating a digital signature typically works:
- The user initiates the signing process by selecting the document they want to sign.
- The software prompts the user to choose the digital certificate they want to use for signing.
- The software then applies the digital signature to the entire document, ensuring its integrity and authenticity.
- The signed document is now ready to be transmitted or shared with others.
It’s important to note that creating a digital signature is not the same as creating an electronic signature. While both serve the purpose of signing digital documents, there are key differences between them. An electronic signature is simply an image of a hand-written signature or a typed name, while a digital signature is based on cryptographic algorithms and offers a higher level of security and authentication.
So, if you want to create a digital signature, make sure you choose a reputable digital signature provider that offers advanced PKI-based solutions. This will ensure that your digital signatures are legally compliant, trusted, and widely accepted across industries.
What is Public Key Infrastructure PKI
Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) is a technology used to ensure the integrity and authenticity of digital documents and transactions. It is widely used in industries such as finance, commerce, and government to establish a trusted and secure environment for transmitting sensitive information.
PKI relies on the use of public and private keys to create digital signatures, which are used to verify the authenticity and integrity of documents. The public key is openly available and can be used by anyone who wants to verify the authenticity of a document. The private key, on the other hand, is kept secret and is used to create the digital signature.
When you want to sign a document using PKI, you use your private key to create a digital signature. This signature is unique to you and ensures that the document has not been tampered with. The digital signature can be verified using your public key, which is widely known and trusted.
PKI relies on a trusted third party called a Certificate Authority (CA) to verify the identities of individuals or organizations. The CA issues digital certificates that bind a public key to a specific entity. These certificates are based on industry standards such as X.509 and are compliant with PKI protocols.
By using PKI, organizations can enforce the authenticity and integrity of their documents. This means that the documents can be legally enforceable, as they can be trusted to have not been tampered with after they have been signed.
One well-known provider of PKI technology is Docusign, which offers a range of solutions for digitally signing and transmitting documents. With Docusign, you can easily send and receive signed documents, knowing that they have been verified and are valid.
In summary, PKI is a standards-based technology that belongs to the world of digital signatures and encryption. It ensures the trustworthiness and integrity of documents by verifying the identity of the signing party and ensuring that the document has not been tampered with. PKI is widely used in industries and businesses that require secure and verified transactions.
What is a Certificate Authority (CA)
In today’s digitally connected world, where we want to send and receive electronic documents that are legally compliant and secure, a digital signature is essential. But how do we verify the integrity of digitally signed documents? This is where a Certificate Authority (CA) comes into the picture.
A Certificate Authority is a trusted third-party organization that is responsible for issuing, revoking, and managing digital certificates. A digital certificate is a unique electronic document that associates a user’s identity with a public key. It is created using a process called Public Key Infrastructure (PKI), which follows advanced and widely accepted standards-based processes.
When you sign a document with a digital signature, the digital certificate associated with your name and signature is used to verify its authenticity and ensure that the document has not been tampered with since it was signed. The CA plays a crucial role in verifying and enforcing the validity of digital certificates, thereby reducing the risk of forgery or fraudulent activities.
So, how does a CA work in practice? Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- The user (the signer) creates a digital certificate using software or a trusted provider.
- The user’s public key is combined with other information, such as their name and organization, to create the digital certificate.
- The user’s digital certificate is then signed by the CA. This process ensures that the CA has verified the user’s identity and guarantees the integrity of the certificate.
- The CA’s digital certificate, also known as the root certificate, is pre-installed in software or operating systems, making it widely trusted.
- When the user wants to sign a document, the software or solution they are using verifies the CA’s root certificate to ensure its validity.
- The user signs the document with their private key, which is securely stored and associated with their digital certificate.
- The signed document, along with the user’s digital certificate, is sent to the recipient.
- The recipient’s software or solution verifies the signer’s certificate using the CA’s root certificate and the public key of the signer.
- If the verification is successful, the recipient can be confident that the document was signed by the specified user and that its integrity has not been compromised.
By relying on a trusted CA, businesses and individuals can ensure that their digitally signed documents are legally compliant and secure. Certificate Authorities, such as DocuSign, provide industry-standard solutions that meet the highest security and regulatory standards.
In summary, a Certificate Authority plays a vital role in the digital signature process by verifying the authenticity of digital certificates and ensuring the integrity of electronically signed documents. It is a trusted third-party organization that reduces the risks associated with forgery and fraudulent activities in today’s digitally connected world.
Why would I use a digital signature
There are many reasons why you would use a digital signature in today’s digitally-driven world. Digital signatures provide a secure and legally binding way to sign and validate documents electronically, making them the go-to choice for many industries and organizations.
One of the most important reasons to use a digital signature is that it gives your documents the authority and unique validation they need to be legally valid. Unlike traditional signatures, digital signatures are not easily forged or tampered with. They use trusted technology and encryption processes to ensure that the signature has not been altered after it has been applied.
When you send a digitally signed document, the recipient can verify the authenticity and integrity of the signature without having to rely on the physical presence of the signer. This can save time and streamline the signing process, especially for businesses that deal with a large volume of documents.
Another key advantage of using a digital signature is the added security it provides. Digital signatures use advanced encryption algorithms to prevent unauthorized access and ensure that only the intended recipients can open and view the document. This helps protect sensitive information and reduces the risk of data breaches.
Using a digital signature also simplifies the process of revoking or updating signatures. If a signature needs to be revoked or updated, it can be done electronically without having to physically track down and destroy paper documents. This can be especially useful for regulated industries that require frequent updates or changes to documents.
So, why should you use a digital signature? Simply put, it offers a faster, more secure, and legally enforceable way to sign and verify electronic documents. In today’s digital age, where almost everything is done online, understanding how digital signatures work and their benefits is essential for individuals and businesses alike.
What digital signature solutions does DocuSign offer
DocuSign offers a range of digital signature solutions that provide tamper-evident protection for your documents. These solutions are well-established in various industries and can be used to meet the legally compliant requirements of electronically signed documents.
When you send a document using DocuSign’s digital signature technology, the integrity and authenticity of the document is verified through a unique certificate. This certificate is associated with the sender’s name and includes all the necessary information to ensure that the document remains secure and compliant.
The digital signature process includes the use of public key infrastructure (PKI) technology, where a sender’s private key is used to create a digital signature, while the recipient’s public key is used to verify the signature. This ensures that the document cannot be tampered with or modified without detection.
DocuSign’s digital signature solutions also go beyond just creating and sending digitally signed documents. They offer a comprehensive platform that includes features such as encryption, secure storage, and compliance with industry regulations. This means that you can trust DocuSign to deliver the highest level of security and integrity when it comes to your important business documents.
Here’s a breakdown of some of the key features and benefits of using DocuSign’s digital signature solutions:
| Certificate Authority (CA) | The use of established certificate authorities ensures the authenticity and integrity of your digitally signed documents. |
| PKI Technology | DocuSign utilizes PKI technology to create and verify digital signatures, providing a secure and reliable method for electronic signatures. |
| Compliance | DocuSign’s digital signature solutions are designed to meet the compliance requirements of various industries and regulations. |
| User Understanding | The user-friendly interface and intuitive processes of DocuSign make it easy for anyone to create, send, and sign digital documents. |
| Security and Integrity | With DocuSign’s digital signature solutions, you can be confident that your documents are protected from tampering or unauthorized access. |
| Global Acceptance | DocuSign is widely recognized and accepted as a trusted provider of electronic signatures around the world. |
In today’s digital world, the use of electronic signatures is becoming more and more prevalent. DocuSign’s digital signature solutions offer the highest level of security, compliance, and convenience, making them the preferred choice for businesses in various industries. So whether you need to sign a contract, submit a legal document, or complete any other important transaction, DocuSign has the digital signature solution that meets your needs.
Are eSignatures based on digital signature technology legally enforceable
eSignatures that are based on digital signature technology have been widely accepted and legally enforceable in many countries. These types of signatures use digital certificates and keys to authenticate and verify the identity of the signer. By using this technology, individuals and businesses can ensure the integrity and authenticity of electronically signed documents.
When an eSignature is created using digital signature technology, it acts as a virtual seal on the document, ensuring that it has not been tampered with or altered in any way. The digital signature is created by a specific software or online solution that utilizes Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) technology. This ensures that the document can only be opened and associated with the specified signer’s private key.
One key difference between eSignatures and digital signatures is that eSignatures do not rely on the use of digital certificates. Instead, eSignature solutions such as Docusign offer their own means of verifying the identity of the signer, ensuring that their acts are legally valid and compliant with industry regulations.
While eSignatures without digital certificates are legally enforceable, there are still security measures in place to ensure the authenticity and integrity of the signed document. For example, Docusign uses a combination of email verification and authentication codes to ensure that the signer is who they claim to be.
So, why are digital signatures not required for eSignatures to be legally enforceable? The reason is that the technology behind eSignatures, such as Docusign, offers other means of verification and validation to ensure the integrity and authenticity of the signed document. These methods have been widely accepted and trusted in the industry.
In summary, eSignatures based on digital signature technology, as well as those without digital certificates, are legally enforceable. Their validity and compliance are ensured through the use of various security measures and verification processes. Whether the signer uses a digital certificate or an eSignature solution like Docusign, the goal is the same: to create a trusted and legally valid electronically signed document.
What is a digital certificate
In today’s digital world, electronic signatures have become widely used in various industries. To ensure the authenticity and integrity of electronic documents, digital certificates play a crucial role. A digital certificate, also known as a public key certificate, is an electronic document that uses a digital signature to verify the identity of the sender and ensure that the document has not been tampered with.
A digital certificate includes key information about the user or organization it is associated with, such as their name, the name of the certificate authority (CA) that issued the certificate, and the certificate’s unique serial number. It also includes a public key that can be used to verify the digital signature.
When a user wants to sign a document using an electronic signature, they can create a digital signature using their private key. This signature is then embedded in the document, along with the user’s digital certificate. The recipient can then use the public key from the certificate to verify the signature and ensure that the document has not been changed or tampered with.
One of the most widely known solutions for digitally signing and validating documents is DocuSign. This platform provides advanced electronic signature solutions that meet the legally compliant requirements in many industries. DocuSign’s digital certificates are associated with a qualified certificate authority, ensuring their trustworthiness and reliability.
In addition to ensuring the integrity of documents, digital certificates also play a crucial role in revoking or invalidating certificates. If a certificate becomes compromised or is no longer valid, it can be revoked by the certificate authority. This revocation information is then passed on to users who rely on the certificate for verification.
By using digital certificates and electronic signatures, organizations can create a secure and trusted environment for their document signing processes. The use of digital certificates reduces the reliance on physical infrastructure and paper-based processes, making it easier and more efficient to sign and verify documents.
So, what does this mean for businesses and individuals? It means that digital certificates and electronic signatures provide a legally compliant and secure way of sending and signing documents. Whether it’s a business contract, a legal document, or any other type of agreement, digital certificates ensure that the document is verified and the integrity of the content is maintained.
In summary, a digital certificate is a crucial part of the digital signature process. It provides the necessary trust and authentication for electronic documents, ensuring that they are legally compliant and secure. So next time you come across a digitally signed document, know that it’s backed by a digital certificate and the signature has been verified using advanced cryptographic techniques.
What is the difference between Advanced Electronic Signature and Qualified Electronic Signature
In the digital world, electronic signatures play a crucial role in ensuring the integrity and authenticity of electronically transmitted documents. There are different types of electronic signatures, including Advanced Electronic Signatures (AES) and Qualified Electronic Signatures (QES), each with its own set of characteristics and capabilities.
Advanced Electronic Signatures (AES) are designed to provide a higher level of security and reliability compared to basic electronic signatures. AES utilizes cryptographic techniques to ensure the integrity of the signed document and identifies the signer based on their unique digital key. This means that an AES is tied to the signer’s identity and can be verified and validated by the recipient. AES is widely recognized and accepted in the industry as a reliable means of electronically signing documents.
On the other hand, Qualified Electronic Signatures (QES) go a step further by providing additional legal validity and enforceability. QES is based on the use of a Qualified Certificate (QC), issued by a trusted Certification Authority (CA). The QC contains the signer’s identification information and is used to verify the authenticity of the signature. QES offers a higher level of assurance, as it requires the signer to undergo a more rigorous identity verification process conducted by the CA.
While both AES and QES provide a means to electronically sign documents, the key difference lies in the level of reliability and legal validity they offer. AES ensures the integrity of the signed document and identifies the signer based on their unique digital key. QES, on the other hand, provides additional legal validity and enforceability by using Qualified Certificates issued by a trusted CA. This means that QES signatures have a higher level of assurance and are more widely accepted in legal and regulatory contexts.
When it comes to using electronic signatures, understanding the differences between AES and QES is important. If you only want to transmit documents electronically and ensure their integrity along the way, AES is a suitable choice. However, if you require a higher level of legal validity and enforceability, such as when signing important legal contracts or sensitive documents, QES is the better option.
So, why should you consider using AES or QES? Here’s a simple guide:
| Advanced Electronic Signature (AES) | Qualified Electronic Signature (QES) |
|---|---|
| Ensures document integrity | Provides additional legal validity and enforceability |
| Reliable and widely accepted | Offers a higher level of assurance and acceptance |
| Signer’s identity can be verified | Identity verification through Qualified Certificates |
| AES belongs to basic electronic signature technology | QES belongs to the more advanced PKI (Public Key Infrastructure) technology |
| Validation and verification processes are based on software | Verification is an open process and involves a trusted CA |
Both AES and QES have their advantages and are suitable for different scenarios. Ultimately, the choice between them depends on your specific needs and the level of legal validity and enforceability required for your documents.
How do digital signatures work
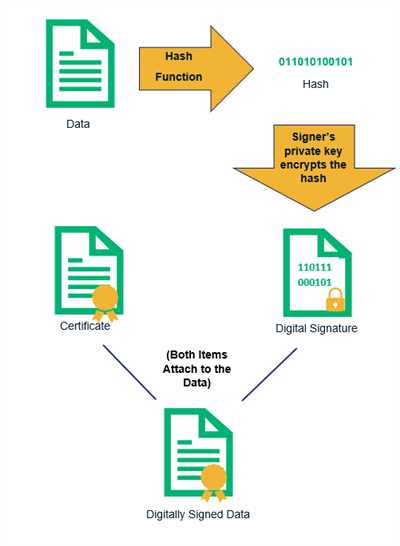
In the digital realm, a digital signature allows you to associate your name with an electronic document, verifying that it is authentic and has not been tampered with. It provides a means to ensure the integrity and authenticity of electronic documents, transactions, and communications.
A digital signature is created by using a technology based on public key infrastructure (PKI). It involves the use of two keys – a private key and a public key. The private key is kept securely by the signer and should never be shared with anyone. The public key, on the other hand, is made available to anyone who wants to verify the signature.
When signing a document, the signer’s software uses their private key to generate a unique digital signature, which includes information about the document that is being signed. This signature is then attached to the document, creating a digitally signed version of it.
To verify the signature and ensure the document has not been tampered with after signing, the receiver uses the signer’s public key. The digital signature is passed through a mathematical algorithm and if it matches the original document, it is considered valid. This process reduces the risk of malicious tampering and provides a trusted means of verifying the authenticity and integrity of digitally signed documents.
Digital signatures are compliant with legal and industry standards, such as the eSignatures Act. They offer a reliable method for organizations and individuals to sign, send, and receive legally binding documents. In industries such as finance, healthcare, and commerce, digital signatures have become an essential part of the infrastructure.
One popular provider of digital signature technology is DocuSign. They offer a secure platform that allows individuals and organizations to electronically sign and send documents. DocuSign’s electronic signatures meet the requirements of qualified signatures and provide a trusted and verified method for signing and transmitting documents.
So, how do digital signatures work? They use a combination of cryptographic keys, encryption technology, and trusted authorities to ensure the integrity, authenticity, and security of electronic documents. Without digital signatures, it would be difficult to provide a reliable method for verifying the identity of signers and protecting the confidentiality and integrity of electronically transmitted information.
In summary, digital signatures play a crucial role in the digital world. They provide a means to verify the authenticity and integrity of documents, reduce the risk of tampering, and offer a trusted method for signing and transmitting information. Understanding how digital signatures work is essential for those who want to use them in their organization or in personal transactions.
What is Public Key Infrastructure (PKI)
Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) is a set of practices, policies, and procedures that provide secure and encrypted communication over the internet. PKI is essential for ensuring the integrity and authenticity of digital transactions, and it plays a crucial role in modern security solutions.
In the context of digital signatures, PKI is utilized to establish the trust and authenticity of the sender. It does so by using cryptographic techniques to create a unique digital signature that can only be verified by the corresponding public key. This ensures that the document or message has not been tampered with and that it originated from the specified sender.
PKI employs a hierarchical structure that includes a Certification Authority (CA) as the main authority. The CA issues digital certificates that bind the identity of an individual or organization to a public key. These certificates are used to verify and validate the signatures and identities of the users. A widely used example of PKI is the implementation of digital signatures by DocuSign, a leading provider of electronic signature technology.
PKI provides a reliable and secure means of establishing trust in electronic transactions, without the need for physical signatures. It ensures the integrity, confidentiality, and non-repudiation of data sent over the internet. PKI processes also include the establishment and revoking of certificates, ensuring that only valid users can create and verify digital signatures.
In industries such as finance, healthcare, and e-commerce, where regulatory compliance is crucial, PKI is an essential part of the security infrastructure. It offers advanced security solutions and acts as a globally recognized standard to ensure the authenticity and legality of digitally signed documents.
What is a Certificate Authority CA
A Certificate Authority (CA) is an integral part of the Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) used to establish the authenticity, integrity, and validity of digital documents, signatures, and certificates in electronic commerce and other online transactions.
CA acts as a trusted third-party provider that issues, verifies, and manages digital certificates, which are used to sign and encrypt documents or establish secure online communication channels. By doing so, a CA ensures that the public keys associated with the digital certificates are valid and belong to the specified organization or user.
When a user wants to send a digitally signed document, they use a CA’s services to create a digital signature. This signature is attached to the document and can be used to verify its authenticity and integrity. In today’s world of electronic commerce and online transactions, digital signatures play a crucial role in ensuring the security of business processes.
By using a CA, businesses can achieve legally enforceable and widely accepted electronic signatures. The CA’s validation process reduces the risk of tampering and provides a means to prove that the document has not been modified or altered after it was signed. These digitally signed documents can be used in both open and closed environments.
There are various certificate authorities available in the market, and some of the most trusted and widely used ones include Docusign, which offers advanced document solutions, and Docusign compliant certificates. These certificates help businesses meet the industry standards and regulations associated with digital signatures.
In summary, a Certificate Authority (CA) is a trusted provider of digital certificates that ensures the validity, integrity, and authenticity of electronic documents and signatures. CA plays a crucial role in today’s electronic commerce by establishing a secure infrastructure that allows users to sign documents electronically and verify their validity.
What is a digital certificate
In today’s world of digital commerce, ensuring trust and security in online transactions is of utmost importance. This is where digital certificates play a vital role.
A digital certificate is an electronic document that acts as an enforceable, trusted credential. It includes a public key, which belongs to a specific entity or organization, as well as other information that verifies and identifies the owner of the certificate.
Digital certificates are based on standards-based Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) protocols and processes, which ensure the validity and authenticity of the certificate. They are issued by a certification authority (CA), a trusted third party that verifies the identity of the certificate holder before issuing the certificate.
When transmitting sensitive data or documents over the internet, such as financial information or legal contracts, it is crucial to use digital certificates. By digitally signing the document using the private key that corresponds to the public key in the certificate, the sender can ensure that the document has not been tampered with or modified during transmission.
One widely used example of a digital certificate is the Qualified Certificate, which meets specified legal requirements and is used in industries such as e-commerce and regulated business activities.
Here’s a step-by-step guide on how digital certificates work:
- The certificate holder generates a pair of cryptographic keys: a private key and a public key.
- The certificate holder sends a certificate signing request (CSR) to a trusted CA, providing information about the entity or organization and the public key.
- The CA verifies the identity of the certificate holder and issues the digital certificate, digitally signing it with the CA’s private key.
- The certificate holder can now use the digital certificate to sign and encrypt documents or to authenticate themselves in various online transactions.
- The recipient of a digitally signed document can verify the authenticity and integrity of the document by using the sender’s public key, which can be obtained from the digital certificate.
- If the digital certificate has been revoked or expired, the recipient can check the certificate revocation list (CRL) maintained by the CA to ensure that the certificate is still valid.
Using digital certificates reduces the risk of malicious tampering or unauthorized access to sensitive data. It provides a way to establish trust and enforce accountability in the digital world.
It’s important to note that a digital certificate is not the same as a digital signature. While a digital certificate is used to verify the identity of the certificate holder, a digital signature is used to verify the authenticity and integrity of a specific document or message.
In summary, a digital certificate is an essential part of ensuring secure and trusted communications in today’s digital world. It acts as a trusted authority, verifying the identity of the certificate holder and enabling secure transmission of sensitive information between parties.

