When it comes to writing a story plot, many students find it challenging to create a compelling narrative. What makes it even harder is that there isn’t always a previous experience to draw upon. So, what is a student to do? Well, one helpful approach is to use a plot diagram.
A plot diagram is a visual tool that helps writers map out the sequence of events in their story. It is based on the common structure of most narratives and can be a valuable resource for any writer. In fact, it is often used in intermediate and college-level writing lessons.
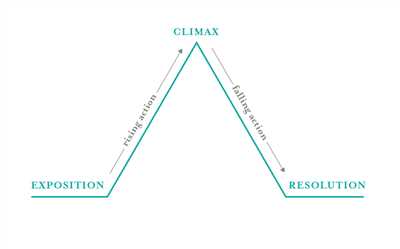
The plot diagram consists of five main parts: exposition, rising action, climax, falling action, and resolution. Each of these parts is significant and leads the story forward in its own way. For example, the exposition sets the stage by introducing the characters, setting, and basic conflict. The rising action includes a series of events that build tension and develop the plot. The climax is the turning point of the story, where the conflict reaches its peak. The falling action follows the climax and shows the aftermath of the conflict. The resolution, also known as the denouement, resolves the conflict and brings the story to a close.
To create a plot diagram, it can be helpful to think about the key traits and actions of your characters. What are their goals and motivations? What obstacles do they face? What choices do they make? By answering these questions, you can start to develop a clear sequence of events that will make up your story plot.
Additionally, it’s always a good idea to check out other sources for inspiration and guidance. There are many websites and books available that provide diagrams and examples of story plots. One of the most recommended sources is the Purdue OWL, where you can find in-depth lessons on how to create effective plots.
Remember, though, that every story is unique, and there isn’t always a one-size-fits-all approach. It’s essential to think creatively and find what works best for your writing style. So don’t be afraid to experiment and explore different plot structures!
In conclusion, understanding how to write a story plot is an essential skill for any writer. By using a plot diagram and thinking critically about your characters and their actions, you can create a compelling narrative that will captivate readers. Keep in mind that there are no strict rules when it comes to writing, so don’t be afraid to take risks and let your imagination soar!
Welcome to the Purdue OWL
Understanding how to write a story plot is essential for any writer. Whether you are a student working on a college essay or a beginner to the world of storytelling, knowing how to create a strong plot can make all the difference in keeping your readers engaged. In this section, we will cover what a plot is, why it is important, and provide you with some tips and techniques to help you develop an interesting and compelling storyline.
A plot is the sequence of events that occurs in a narrative. It is the framework within which the story unfolds and the actions of the characters take place. Think of it as the skeleton of your story; it gives your narrative structure and allows your readers to follow along with the events and experiences of your characters.
When crafting a plot, it is important to think about the needs of your story. Consider what your characters want, what obstacles they face, and how they ultimately resolve their conflicts. A plot should have a clear beginning, middle, and end, with each section building upon the previous one. This progression not only helps to keep your readers engaged but also contributes to the overall sense of depth and development within your story.
There are several key elements that can help make a plot more interesting and engaging. One of these elements is the antagonist, the character or force that opposes the protagonist. The conflict between the protagonist and the antagonist creates tension and drives the plot forward. Additionally, adding unexpected twists and turns to your plot can keep readers guessing and make your story more unpredictable.
In addition to understanding the elements of a plot, it can also be helpful to visualize your storyline using diagrams such as the plot pyramid or narrative sequence. These tools provide a visual representation of the key events in your story, helping you to see the overall structure and flow of your plot.
At the Purdue OWL, we have provided resources and guidance to help you better understand and develop your story plot. Whether you are a beginner looking for a starting point or an intermediate writer seeking to refine your skills, we have the tools and advice to help you create a compelling and well-structured plot. You’ll find lessons on character development, plot progression, and plot twists, as well as tips on how to make your plot more engaging and memorable.
In conclusion, a strong plot is crucial for any story, whether it be a short literary piece or a full-length novel. It is what keeps readers engaged and invested in your narrative. By understanding the key elements of a plot and utilizing techniques to make it more interesting and unpredictable, you can create a story that captivates your readers and leaves a lasting impact.
What is a plot diagram
A plot diagram is a visual representation of the narrative structure of a story. It’s a tool that helps writers and readers understand the sequence of events that occur in a story. Plot diagrams are commonly used in literature classes, from elementary school all the way up to college, to help students analyze and understand the structure of a story.
A plot diagram typically consists of five key elements:
- Exposition: This is where the story begins and the setting, characters, and main conflict are introduced. It provides the background information that readers need to understand the story.
- Rising Action: This is a series of events that build suspense and lead up to the climax. It’s where the main character faces obstacles and conflicts in their journey.
- Climax: This is the turning point of the story, where the conflict reaches its peak. It’s the most intense and exciting part of the story and often reveals the protagonist’s true traits.
- Falling Action: After the climax, the story begins to wind down. Loose ends are tied up, and the main character starts to resolve the conflict.
- Resolution: This is the end of the story, where the conflict is fully resolved and the loose ends are all tied up. The resolution provides closure to the story and allows the readers to reflect on the events.
A plot diagram helps writers keep track of the events in their story and ensures that the narrative flows smoothly. It helps them understand how different actions and events contribute to the overall plot, and how they can structure their story to maximize suspense and reader engagement.
For readers, plot diagrams provide a helpful visual aid that allows them to see the overall structure of a story. It helps them understand the sequence of events and how they relate to each other. Plot diagrams can also make it easier for readers to identify the main theme or message of the story, as they can see how the actions and conflicts lead to the resolution.
Overall, plot diagrams are a valuable tool for both writers and readers. They provide a sense of organization and structure to the story, making it easier to understand and analyze. Whether you’re a student working on a literary essay or just someone who wants to enjoy a good story, plot diagrams can help enhance your experience and appreciation of storytelling.
Lesson 5: How to Plot a Short Story

Plot is an essential element of any short story. It is the sequence of events that unfold in a story, leading to a resolution. Understanding how to create a strong plot is crucial for writers at every level, from beginner to intermediate.
In the previous lesson, we covered the basics of plot and how it fits into the overall structure of a story. Now, let’s dig deeper into the components of a plot to help you develop a more in-depth understanding.
Think of the plot as a journey that your characters embark on throughout the story. The plot should have a beginning, middle, and end. It should include a conflict or problem that the main character, also known as the protagonist, needs to resolve.
The antagonist, on the other hand, is the character or force that opposes the protagonist and creates obstacles for them along the way. This could be a person, a group of people, nature, society, or even an internal struggle within the protagonist themselves. The antagonist is essential for building tension and conflict in the story.
When working on the plot, consider the actions and decisions that your characters make. These actions should be significant and drive the story forward. Each event should lead to the next, creating a sense of cause and effect.
To help you visualize the plot, you can use diagrams such as the “pyramid” or “Hermione diagram”. These diagrams provide a clear structure for mapping out the key events of your story.
In plotting a short story, it’s important to keep the length in mind. Short stories have a limited word count, so make sure to focus on the most essential and impactful events. You don’t have as much space to explore subplots or go into great depth with your characters and their experiences.
A well-crafted plot will always have a strong sense of theme. The theme is the main idea or message that the writer wants to convey to the readers. It adds depth and meaning to the story, making it more memorable and impactful.
As an intermediate writer, it’s important to study and analyze plots from different sources. Read short stories, essays, and literary works to understand how other writers have used plot effectively. The more you expose yourself to different plots, the more you’ll expand your understanding and develop your own style.
Remember, writing a compelling plot requires practice. Don’t be afraid to experiment and take risks with your storylines. Stay true to your characters and their traits, and let their actions and decisions guide the plot. With time and experience, you’ll become a master at crafting engaging and memorable plots.
For further guidance and writing resources, check out the Purdue Online Writing Lab (OWL) and other educational sources that offer lessons and exercises for plot development. With dedication and hard work, you can create captivating plots that will leave your readers wanting more.
Welcome to Lesson 5 on how to plot a short story! In this lesson, we’ll be diving into the nuts and bolts of creating a compelling plot. Whether you’re a beginner or an intermediate writer, these lessons will help you develop your storytelling skills and take your writing to the next level. Let’s get started!
What’s Next

Now that you have a basic understanding of how to create a story plot, what’s next? There are a few key steps to take in order to build a strong and engaging plot that will captivate readers.
1. Develop your characters: The key to creating a compelling story is to have well-developed characters that readers can care about. Give your protagonist strengths, weaknesses, and personal goals that the readers can relate to. Don’t forget about the antagonist – a strong and formidable opponent can make the conflict more interesting.
2. Create a theme: A theme is the central idea or message of your story. It often explores universal human experiences, such as love, friendship, or the struggle between good and evil. Think about what you want your story to say and how you can use the plot to convey that message.
3. Establish a setting: Your story should take place somewhere, and the setting can significantly impact the plot. Whether it’s a small town or a mythical kingdom, the setting can provide opportunities and limitations for the actions of your characters.
4. Build on the previous events: Remember, a plot is a sequence of events that occur one after another. Each event should connect to the previous one and lead to the next. This sense of cause and effect is what keeps the readers engaged and invested in the story.
5. Add depth and complexity: Don’t be afraid to add twists, turns, and layers to your plot. Surprise the readers with unexpected events, reveal hidden motivations, and explore the complexity of your characters’ emotions. This will make your story more intriguing and memorable.
6. Resolve the conflict: No plot is complete without a resolution. The conflict or problem presented in the story needs to be resolved in a satisfying way. Avoid abrupt or unsatisfactory endings by giving your readers a sense of closure and fulfillment.
Remember, writing a story plot is an art that takes practice and refinement. The more you work on it, the better you’ll get. Don’t be afraid to experiment and try new things, and always keep learning from other writers and analyzing their plots.
For more guidance on writing, check out the resources provided by Purdue owl, a trusted source for writing tips and lessons. They have a great guide on how to write a plot diagram, which can help you visualize the structure of your story.
Sources
When it comes to writing a story plot, there are several sources that can help you develop a strong and engaging narrative. Here are some key sources to consider:
- Readers: One of the best sources of inspiration for your story plot is your readers. Pay attention to what captivates them, what hooks them in, and what keeps them engaged. Take note of the types of plots and themes that resonate with your target audience, and use that knowledge to craft a compelling story.
- Literary works: Reading other literary works can provide valuable insights and ideas for your own story plot. Explore different genres and authors to broaden your understanding of storytelling techniques. Look for common plot structures, character traits, and narrative devices that you can adapt and incorporate into your own writing.
- Previous experiences: Your own life experiences can serve as a rich source of material for your story plot. Draw from personal anecdotes, significant events, or lessons learned to create authentic and relatable narratives. By infusing your own emotions and insights into your writing, you can create a deeper connection with your readers.
- Observation: Paying attention to the world around you can be a great source of inspiration. Observe people, places, and events in your daily life, and think about how they could be adapted and transformed into fictional scenarios. Look for interesting settings, intriguing characters, or thought-provoking situations that can serve as the foundation for your story plot.
- Writing resources: There are numerous writing resources available that can help you develop your story plot. Websites like Purdue Owl provide valuable guidance on various aspects of writing, such as plot structure, character development, and narrative techniques. Take advantage of these resources to enhance your storytelling skills.
Remember, a strong story plot is one that not only keeps the reader engaged but also makes them think, feel, and empathize with the characters. By drawing inspiration from various sources and putting in the time and effort to develop a well-structured plot, you can create a memorable and impactful story.