When it comes to managing different websites or creating additional layers of content online, subdomains can be a useful solution. Subdomains are a way to divide your main domain into separate addresses, allowing you to host multiple websites under the same domain name. This article will explain what a subdomain is and how to create and manage one for your website.
In simple terms, a subdomain is a part of a larger domain. It is a prefix that appears before the main domain and is separated by a dot. For example, if your main domain is “mywebsite.com,” you can create a subdomain like “blog.mywebsite.com.” The subdomain acts as a separate website with its own content and settings, while still being connected to the main domain.
So, why would you want to use a subdomain? There are a few reasons why subdomains are popular:
- Subdomains allow you to open multiple websites with different content on the same hosting account. This is useful if you want to keep certain websites separate from others or if you have different projects that require their own online presence.
- Some content management systems, like WordPress, support subdomains by default. This means that you don’t need to install additional plugins or make complex settings to create a subdomain within your WordPress website.
- Subdomains can also be used to create a memorable and easy-to-type web address. For example, if your main domain is “mywebsite.com,” you can create a subdomain like “shop.mywebsite.com” for your online store. This makes it clear to visitors what they can expect from each section of your website.
To start using subdomains, you need to follow these steps:
- Check if your current hosting provider supports subdomains: Not all hosting providers offer subdomains, so you should check with your provider or review their support documentation to see if it is supported.
- Create a subdomain: Once you are sure that your hosting provider supports subdomains, you can create one through your hosting account’s control panel or settings. This process may vary depending on your hosting provider, so it is best to refer to their documentation for specific instructions.
- Set up DNS entries: After creating a subdomain, you will need to set up DNS records to point the subdomain to the correct location. This involves creating a DNS record that associates the subdomain with the IP address or server where the subdomain is hosted.
- Manage the content of your subdomain: Once the subdomain is set up and the DNS entries are in place, you can start managing the content of your subdomain. This can include creating new web pages, editing existing content, or installing a content management system like WordPress on the subdomain.
In conclusion, subdomains are a useful way to manage multiple websites or create additional layers of content online. By following the steps outlined in this article, you can easily create and work with subdomains for your website, making it more organized and user-friendly.
Sources: www.stackoverflow.com
- What Are Subdomains and How to Create One + the Differences Between Domains and Subdirectories
- 1 Answer 1
- How To Install WordPress on a Subdomain
- 1 Create a Subdomain
- 2 Install WordPress To That Subdomain
- Edit Your DNS Settings
- Domain hosted by your current Square account
- Domain hosted by a different Square account
- Domain hosted by a third party
- What’s in this article
What Are Subdomains and How to Create One + the Differences Between Domains and Subdirectories
Subdomains are a way to organize and structure your website by adding a prefix to your main domain name. They can be used to create separate sections or divisions within a website. For example, if your main domain is “example.com,” you can create a subdomain called “blog.example.com” for your blog.
There are some key differences between domains and subdirectories that should be noted. Domains are the full address of a website, such as “example.com.” Subdirectories, on the other hand, are extensions of a domain and are placed after the main domain name, such as “example.com/blog.” The main difference is that subdomains create a separate “layer” or section within a website, while subdirectories are part of the main website content.
So, how do you create a subdomain? Here are some steps to follow:
- Log in to your hosting account or your domain registrar’s website.
- Find the section for managing your domain settings.
- Look for an option to create a subdomain.
- Select the option to create a subdomain and enter the desired name for your subdomain (e.g., “blog” for “blog.example.com”).
- Choose the domain under which you want to create the subdomain.
- Save the settings or submit the form to create the subdomain.
Once you have created the subdomain, you will need to set up the necessary DNS entries to point the subdomain to the correct server. This can usually be done through the DNS settings provided by your hosting provider or domain registrar. If you are unsure about how to do this, consult the support documentation or contact customer support for assistance.
It’s important to note that creating a subdomain does not automatically create a new website. It simply sets up an additional address that can be used to access specific content within your current website. The content for the subdomain will still need to be created and managed separately.
Subdomains can be used for various purposes, such as creating a separate online store, a forum, or a blog. They can also be helpful for managing different languages or regions of a website. For example, you can have “en.example.com” for English content and “fr.example.com” for French content.
In summary, subdomains are a useful tool for organizing and managing your website. They provide a way to create separate sections or divisions within your site. By following the steps outlined in this article, you can easily create a subdomain and set it up to work with your current website.
Sources:
1 Answer 1
To create a subdomain, you will need to edit your domain’s DNS settings. Here are the steps you would typically take to create a subdomain:
1. First, make sure you have a hosting account or a third-party hosting provider where your main website is hosted. Let’s call this your “root domain.”
2. Log in to your hosting account and find the DNS settings. Different hosting providers have different ways of managing DNS, so consult their documentation or support for specific instructions.
3. In the DNS settings, you will usually find an option to create a new record. Select this option.
4. When creating the new record, select the type as “subdomain” or “A record” depending on the hosting provider’s terminology.
5. In the “Name” or “Host” field, enter the subdomain name you want to create. For example, if you want to create a subdomain called “blog” for your website, enter “blog” in this field.
6. In the “Address” or “Points to” field, enter the IP address where you want the subdomain to point to. This could be the same IP address as your root domain or a different one if you want the subdomain to be hosted on a different server.
7. Save the record, and the subdomain should now be created. It may take some time for the changes to propagate, so be patient.
Now, when someone enters the subdomain address (e.g., blog.yourdomain.com), it will point to the specified IP address, and you can host different content or create a separate website on the subdomain.
It’s important to note that there are some differences between subdomains and subdirectories. Subdomains have their own separate hosting environments and can be hosted on different servers, while subdirectories are part of the main website and share the same hosting environment.
In some cases, if you’re using a CMS like WordPress, you may also need to edit the settings within the CMS to make sure it recognizes the subdomain and serves the appropriate content.
I hope this helps! Let me know if you have any more questions.
How To Install WordPress on a Subdomain

When you want to create a new website but don’t want it to be part of your main domain, one option is to use a subdomain. This allows you to have a separate website with a distinct address that is still connected to your main domain. In this article, we will explain how to install WordPress on a subdomain.
Before we dive into the steps, let’s clarify what a subdomain is. A subdomain is a third-level domain that is part of a larger domain. It is denoted by adding a prefix to the main domain, separated by a dot. For example, if your main domain is “example.com”, a subdomain could be “blog.example.com”.
Now, let’s get started with the installation process:
Step 1: Create a Subdomain
The first thing you need to do is create a subdomain. This can usually be done through your hosting provider’s control panel or DNS settings. Make sure to select the option to create a subdomain and specify the desired name.
Step 2: Edit DNS Settings
After creating the subdomain, you may need to edit the DNS settings to ensure that it points to the correct location. This could involve adding an “A” record or a “CNAME” record, depending on your hosting provider. Consult your hosting provider’s support or documentation for specific instructions.
Step 3: Install WordPress
Once the DNS settings are updated, you can proceed with installing WordPress on your subdomain. Most hosting providers offer a one-click WordPress installation option, which makes the process relatively simple. Follow the on-screen instructions to complete the installation.
Step 4: Manage Your Subdomain
With WordPress installed on your subdomain, you can now manage it like any other website. Login to your WordPress admin dashboard and start customizing the design, adding content, and installing plugins to enhance the functionality of your subdomain.
In conclusion, installing WordPress on a subdomain involves creating the subdomain, editing DNS settings, and installing WordPress on the subdomain. Make sure to follow the specific steps provided by your hosting provider, as the process may vary slightly. By using a subdomain, you can have multiple websites hosted under one domain while keeping them separate and distinct.
Sources: www.stackoverflow.com
1 Create a Subdomain
If you want to have a separate section of your website that is hosted on a subdomain, there are a few steps you need to follow. In this article, we will explore how to create a subdomain.
A subdomain is like an additional chapter of your website. For example, if your main domain is example.com, you can create a subdomain like blog.example.com, where you can host your blog content.
In order to create a subdomain, you will need to have access to the DNS settings for your domain. DNS is short for Domain Name System, and it is responsible for matching domain names to the IP addresses of the servers where websites are hosted.
The first step is to log in to your hosting account or domain registrar that manages your DNS settings. Once you are logged in, navigate to the settings page for your domain.
Look for an option to manage DNS settings or DNS records. Depending on your hosting provider, this could be located in different places. If you are using a popular hosting provider like WordPress or SquareSpace, you might find it under the Domains or DNS section.
Once you have found the DNS settings, you will need to locate the section where you can add DNS records. There should be an option to add a new record.
In the record type, select the option for creating a subdomain. In the “Name” field, enter the name of the subdomain you want to create, such as “blog” for blog.example.com.
In the “Type” field, select the record type that corresponds to the kind of content you want to host on the subdomain. For example, if you want to host a website on the subdomain, you would select the “A” record type.
In the “Address” field, enter the IP address of the server where you want the subdomain to point to. This could be the same IP address as your main domain or a different one depending on your hosting setup.
Finally, save the DNS record and wait for the changes to propagate. It may take some time for the changes to take effect, but once they do, your subdomain will be created and ready to use.
It’s important to note that creating a subdomain does not automatically install any third-party software or set up a separate hosting account. It simply creates a new address that points to a specific folder on your current hosting account. So, if you want to install WordPress or any other content management system on your subdomain, you will need to do that separately.
Now that you know how to create a subdomain, you can have multiple sections within your website, each with its own unique subdomain address.
2 Install WordPress To That Subdomain
Once you have set up the subdomain for your website, the next step is to install WordPress on that subdomain. Here’s how you can do it:
- First, make sure you have a hosting account that supports subdomains. If you don’t have one, sign up for a hosting service.
- Create a new subdomain in your hosting account. This can usually be done through the hosting provider’s control panel or dashboard. Make sure to select the subdomain option and enter the desired subdomain name.
- Once the subdomain is created, you will need to assign it a separate root folder. This is where the WordPress files will be installed. You can either use the default root folder or create a new directory within the root folder for the subdomain.
- Next, you will need to edit your DNS settings. Open your DNS settings through your hosting provider’s control panel or through a third-party DNS management service. Add a new record with the subdomain name as the host and the IP address of the hosting server as the value. If you are unsure of the IP address, you can usually find it in the hosting account settings or by contacting your hosting provider.
- After updating the DNS settings, you need to wait for the changes to propagate. This process can take anywhere from a few minutes to several hours, so be patient.
- Once the DNS changes have taken effect, you can proceed with the WordPress installation. Install WordPress on the subdomain just like you would for a regular domain. You can use the WordPress installer provided by your hosting provider or follow the manual installation steps provided by WordPress.
- During the installation process, make sure to select the subdomain you created as the installation location. This will ensure that WordPress is installed on the correct subdomain.
- After the installation is complete, you can log in to your WordPress dashboard and start managing the content of your subdomain website.
- Keep in mind that each subdomain is treated as a separate website, so you can use different themes, plugins, and settings for your subdomain compared to your main domain.
- If you have multiple subdomains and want to manage them all from one WordPress installation, you can use a WordPress multisite setup. This allows you to create and manage multiple websites within a single WordPress installation.
By following these steps, you can easily install WordPress on your subdomain and start building your website. Remember to update the DNS settings, create the subdomain, and select the correct installation location during the WordPress installation process.
Edit Your DNS Settings
If you want to use subdomains for your website, you’ll need to edit your DNS settings. DNS, or Domain Name System, is the layer on top of servers that translates a domain name (such as example.com) into an IP address where the website is hosted. By adding a subdomain, you can create a separate section of your website with its own unique address.
To edit your DNS settings, you’ll first need to access your DNS management account. Most popular hosting providers have their own DNS management interface, where you can make changes to your DNS records. If you’re not sure where to go, check your hosting provider’s support documentation or contact their customer support team for guidance.
Once you’re in your DNS management account, find the section where you can edit your DNS records. This may be labeled as “DNS settings” or “DNS management”. The exact steps and interface will vary between hosting providers, but the general process is similar.
Look for an option to add a new DNS record. In this case, you want to create a subdomain, so select the “Add Record” or “Add Subdomain” option. Enter the desired subdomain name in the provided field. For example, if you want to create a subdomain called “blog” for your website, enter “blog” in the field.
Next, you need to specify the type of DNS record you want to create. The most common type is an “A” record, which associates a domain name with an IP address. This is typically the type of record used for subdomains. Other types of DNS records, such as “CNAME” or “TXT”, may be used for different purposes.
After selecting the record type, enter the IP address where you want the subdomain to point to. This could be the same IP address as your main domain or a different one, depending on how you want your subdomain to work. If you’re not sure what IP address to use, consult your hosting provider or refer to their documentation.
Once you’ve entered the subdomain name and the IP address, save the DNS record. The changes may take some time to propagate, so be patient. You can use online tools like WhatsMyDNS.net to check if the DNS record has propagated to different DNS servers around the world.
After the DNS record has propagated, you can start using your subdomain. You can install a separate website or host content in subdirectories under the subdomain. For example, if you created a subdomain called “blog”, you can install WordPress or host your blog content under “blog.example.com”.
It’s important to note that subdomains are different from subdirectories. While a subdomain creates a separate website with its own address, a subdirectory is simply a folder within your main domain. For example, “example.com/blog” is a subdirectory, while “blog.example.com” is a subdomain.
Lastly, make sure to update any applicable settings within your website’s CMS or hosting account to support the new subdomain. For example, if you’re using WordPress, you may need to update the site address or settings to reflect the new subdomain.
In conclusion, if you want to use subdomains for your website, you’ll need to edit your DNS settings. This is done by adding a new DNS record for the desired subdomain and specifying the IP address where it should point to. After the DNS record has propagated, you can start using your new subdomain to host additional content or create a separate website.
Domain hosted by your current Square account
If you have a website hosted by your current Square account, you may want to use a subdomain for additional content or to create a separate section of your website. Subdomains are different from subdirectories in that they have their own unique address, noted before the root domain name. For example, if your main website is www.example.com, a subdomain could be blog.example.com.
When it comes to hosting your domain with Square, you can’t directly edit DNS settings or create subdomains. However, there are ways to work around this limitation. One common method is to use a third-party hosting service that supports subdomains. You would simply create the subdomain in your hosting account and edit the DNS entries to point to your Square website.
If you are using WordPress, there is a popular plugin called “WordPress.com Enterprise” that allows you to easily manage subdomains within your Square website. This plugin bridges the gap between Square’s hosting limitations and the functionality you would have with a traditional hosting provider.
Here are the steps you would need to follow if you want to use a subdomain with your Square account:
- First, select a hosting provider that supports subdomains and sign up for an account.
- Once you have your new hosting account, go into the settings and find the option to create a subdomain.
- Create the subdomain and make sure it is pointing to your Square website by editing the DNS records. You may need to add a CNAME record or a CNAME-like record depending on your hosting provider.
- After the DNS changes have propagated, your subdomain should be live and accessible.
- Now, you can create and manage content for your subdomain separately from your main Square website.
It’s important to note that while using a subdomain allows you to have additional content or sections on your website, it does not create a completely separate website. The content and settings between the main domain and the subdomain are still closely tied together.
If you’re not familiar with setting up subdomains and managing DNS records, it may be helpful to consult with a professional or reference online sources such as Stack Overflow for guidance.
In summary, if you want to use a subdomain with your Square account, you would need to select a hosting provider that supports subdomains, create the subdomain, and edit the DNS records to point to your Square website. Keep in mind the differences between subdomains and subdirectories, and make sure you understand the limitations and how to work around them.
Domain hosted by a different Square account
If you have a website hosted on Square, but it is currently hosted by a different Square account, you will need to make some changes to your DNS settings in order to use a subdomain. This article will guide you through the steps you need to take to manage your subdomain hosted by a different Square account.
First, you need to make sure that you have the correct DNS settings in place. In most cases, you will need to edit the DNS record for your subdomain. You can find detailed instructions on how to do this on the Square support website or on online forums like Stack Overflow.
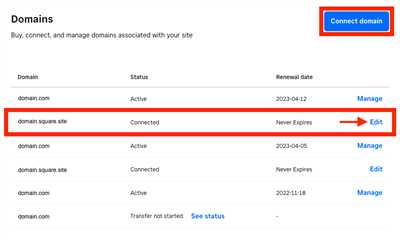
Once you have the correct DNS settings, you can follow these steps to manage your subdomain hosted by a different Square account:
- Select the website that you want to manage from your Square account dashboard.
- Open the “Domains” tab in the website settings.
- Click on the “Add custom domain” button.
- In the input field, enter your subdomain.
- Click on the “+” button to add the subdomain.
- If there are any conflicts between your current DNS settings and the Square account hosting your subdomain, you will see a warning message. You will need to resolve these conflicts before proceeding.
- Once you have resolved any conflicts, click on the “Create domain entry” button to create the subdomain.
- You will now see the subdomain listed under “Your domains” in the website settings.
- To install your website on the subdomain, you will need to follow the instructions provided by your website provider. This may involve updating your DNS settings or configuring your hosting account.
It is important to note that there are some differences between hosting a subdomain on Square and hosting it on a different account. When you host a subdomain on Square, all your website content will be served from the same Square servers. However, if you host your subdomain on a different account, your website content may be served from additional servers.
If you have any further questions or need additional support, you can reach out to the Square support team or refer to the documentation and resources available on their website. They can provide you with more information on how to manage subdomains hosted by a different Square account.
Domain hosted by a third party

If you have a domain hosted by a third-party provider, you may need to make some modifications to your DNS settings in order to use subdomains. These steps will vary depending on the hosting provider, but we will outline the general process below.
1. First, you will need to log in to your account with the third-party hosting provider. Once you are logged in, look for a section where you can manage your DNS settings. This is often labeled “DNS” or “DNS Management”.
2. Open the DNS settings for the domain you want to create a subdomain for. This is usually done by clicking on the domain name or an edit button next to it.
3. In the DNS settings, look for an option to add a new record. This is where you will create the subdomain. The exact wording and location of this option will vary between hosting providers.
4. In the record creation form, you will typically see a few fields that need to be filled out. The first one is the “Type” field, where you will usually select “A” or “CNAME”. The second field is the “Name” field, where you will enter the subdomain name (e.g., “blog” for “blog.yourdomain.com”).
5. In the “Address” or “Destination” field, you will enter the IP address or hostname of the server or website that you want the subdomain to point to. This could be a different IP address than your main domain if the subdomain needs to point to a different server.
6. Once you have filled out all the necessary fields, save the record. It may take some time for the changes to propagate across the DNS servers, so be patient.
7. After the changes have propagated, you can test if the subdomain is working by opening your web browser and navigating to the URL of the subdomain (e.g., “blog.yourdomain.com”). If you see the content or website that you were expecting, then the subdomain has been successfully created and pointed to the correct server or website.
It’s important to note that there are some differences between using subdomains and subdirectories. While both can be used to organize content on your website, subdomains create a separate address for each section of your website, while subdirectories are included as part of your main domain address.
If you are using popular website platforms such as WordPress, you may not have to go through these steps manually. Many hosting providers offer automatic installations of WordPress and other popular platforms, which handle the creation and configuration of subdomains for you.
If you need additional support or have specific questions about your hosting provider, it’s best to reach out to their customer support. They will be able to provide you with the most accurate and up-to-date information for your specific situation.
Sources used: www.stackoverflow.com
What’s in this article
- Introduction to subdomains
- The differences between subdomains and subdirectories
- Why and when you might want to use a subdomain
- How subdomains work
- Creating a subdomain
- Managing subdomains on popular hosting platforms
- Setting up DNS records for a subdomain
- Common issues when working with subdomains
- Additional resources and further reading
In this article, we would explore the concept of subdomains and their usage. Subdomains are a type of domain that are created under an existing domain. They allow you to organize and manage different sections or websites within a single domain. Many websites utilize subdomains to separate their content into different categories or to host various applications.
Understanding the differences between subdomains and subdirectories is important. While both can be used to organize content, they have some key distinctions. Subdomains function as separate websites with their own root directory, while subdirectories exist within the main domain’s root directory. This means that subdomains have their own set of files and settings, making them more suitable for larger or distinct sections of a website.
If you have a website with multiple sections or want to host different types of content, using a subdomain can be a great solution. It allows you to keep everything separate while still managing them under one domain. Additionally, for websites that cater to different regions or languages, using separate subdomains can be a good way to serve localized content to your visitors.
To create a subdomain, you will need to go through a few steps. First, you need to make sure that your hosting provider supports subdomains. Most hosting providers offer this feature, but it’s always good to double-check. Once you confirm that subdomains are supported, you can typically create them through your hosting account’s dashboard or control panel.
In terms of DNS settings, creating a subdomain involves adding an additional DNS record. You will need to select the type of record (often an “A” record for IPv4 addresses or a “CNAME” record for aliases), specify the subdomain name, and point it to the IP address or domain name of the server where the subdomain will be hosted. This can usually be done through your domain registrar’s website or DNS management interface.
Some potential issues to be aware of when working with subdomains include configuring the proper server settings, ensuring that your content is correctly organized within the subdomain’s root directory, and troubleshooting any DNS issues that may arise. Additionally, if you are using a third-party platform like WordPress, you may need to edit some settings to ensure that the subdomain functions correctly.
Overall, subdomains are a useful tool for managing different sections or websites within a single domain. They provide a way to keep your content organized, serve localized content, and create distinct online identities. By understanding how subdomains work and following the necessary steps, you can effectively create and manage your subdomains to enhance your online presence.
To learn more about subdomains, DNS settings, and other related topics, you can refer to the following resources: