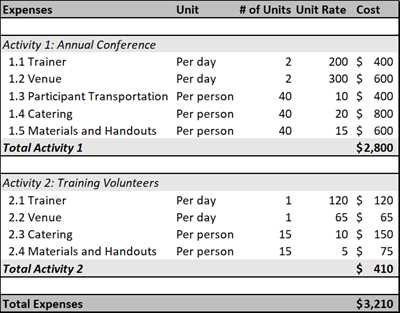
Creating a budget plan is a critical step in managing your personal or business finances. A well-designed budget can help you keep track of your expenses, allocate resources effectively, and achieve your financial goals. However, writing a budget plan can be a daunting task, requiring time, effort, and clarity on your financial needs.
Before you start writing your budget plan, it is important to take some time to think about what you want to achieve and what resources you have available. Consider your income, man-hours, and expenses to get a clear understanding of your financial situation. This will help you make informed decisions and prioritize your spending.
Once you have a clear picture of your financial needs, you can start organizing your budget plan. One tip is to break down your expenses into different categories, such as fixed expenses (e.g., rent, utilities), variable expenses (e.g., groceries, entertainment), and miscellaneous expenses. This allows you to allocate your resources more effectively and identify areas where you can cut back if needed.
It’s also important to note that your budget plan should be flexible and adaptable to changes. For example, if you’re running a business, you may need to adjust your budget based on the market conditions or the performance of your products or services. Similarly, if you’re working for a non-profit organization, you may need to consider the impact of donor funding and grants on your budget plan.
In addition, when writing your budget plan, it’s helpful to have a source of external input. This can come from stakeholders, government agencies, or financial advisors who can provide insights and guidance. Their expertise can help you ensure that your budget plan is realistic, achievable, and aligned with your goals.
In summary, creating a budget plan is an essential task for individuals and organizations alike. By taking the time to think about your financial needs, organize your expenses, and seek external advice, you can develop a budget plan that will help you effectively manage your resources, cover your expenses, and achieve your financial goals.
How to make a budget

A budget is a financial plan that helps individuals, businesses, and organizations manage their expenses and set financial goals. Whether you are budgeting for personal use or developing a budget proposal for a project, it requires careful planning and monitoring to stay on track.
To get started with budgeting, the following tips will help you develop a strong budget:
1. Think about your income:
When creating a budget, it is important to consider your sources of income. This can include your salary, any additional income, or funding from external sources. Having a clear understanding of your income will help you determine how much you can allocate towards different expenses.
2. Categorize your expenses:
Divide your expenses into different categories, such as housing, transportation, groceries, entertainment, and savings. This will give you an overview of where your money is going and allow you to identify areas where you can cut back if needed.
3. Develop a monthly budget:
Creating a monthly budget allows you to have a clear idea of how much you can spend on each category every month. It helps you prioritize your expenses and ensures that you don’t overspend.
4. Monitor your spending:
Keep track of your expenses and compare them to your budget regularly. This will help you identify any overspending and make adjustments as needed.
5. Set savings goals:
Allocating a portion of your budget towards savings is important to create an emergency fund or work towards your financial goals. It is advisable to save at least 10% of your income each month.
6. Plan for unexpected expenses:
Include a category in your budget for unexpected expenses, such as medical emergencies or home repairs. This will help you be prepared financially for any unforeseen situations.
7. Seek help if needed:
If you find budgeting challenging or need assistance with developing a budget, there are organizations and workshops that can provide guidance and support. Don’t hesitate to reach out for help.
By following these budgeting tips, you can create a clear and effective budget that covers your expenses and helps you work towards your financial goals. Remember to regularly review and update your budget as your income and expenses change.
What is a business budget
A business budget is a clear and detailed financial plan that outlines the expected income and expenses for a given period of time, usually monthly or annually. It allows organizations and businesses to track their financial health and make informed decisions based on the financial information provided.
Creating a budget requires organizing and developing a comprehensive list of all the expenses that the business may incur. This includes salary expenses, office rent, utilities, miscellaneous expenses, and any other costs associated with running the business. It is important to note that budgets are not set in stone and can be adjusted as needed.
One critical aspect of creating a budget is understanding the needs and goals of the business. It is important to involve key stakeholders and decision-makers in the budgeting process to get their input and ensure that the budget aligns with the overall goals and objectives of the organization.
When developing a budget, it is also important to consider any potential emergency situations that may arise. Allocating a portion of the budget to an emergency fund is a good practice, as it provides a financial buffer in case unexpected expenses occur.
Business budgets can be used by organizations of all sizes, whether they are small local businesses, non-profit organizations, or large corporations. Regardless of the size or type of organization, having a budget in place allows for greater clarity and understanding of the financial health of the business.
One tip for creating a budget is to break it down into line-item expenses. This allows for better tracking and understanding of where the funds are being allocated. It is also important to keep track of any in-kind donations or resources that may be provided to the business.
When it comes to budgeting, some organizations may prefer to work with a fiscal year, while others may work with a calendar year. It is important to determine the budgeting cycle that works best for the organization and stick to it.
If you’re unsure about how to start budgeting, there are many resources and tips available to help guide you through the process. Some organizations or donors may provide templates or examples that can be used as a starting point. Additionally, there are budgeting software and online tools that can assist in organizing and managing budgets.
In conclusion, a business budget is a critical tool for any organization or business. It allows for better financial planning, tracking, and decision-making. By creating a clear and comprehensive budget, businesses can better understand their financial needs and allocate resources accordingly.
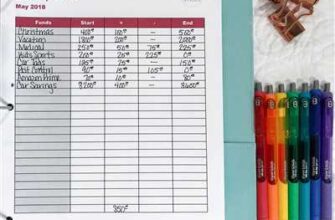
Create a list of monthly expenses
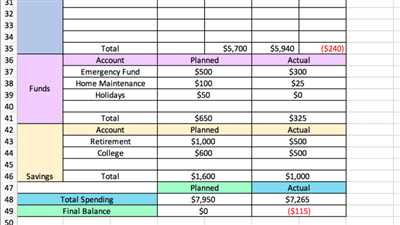
When creating a budget plan, it is important to have a clear understanding of your monthly expenses. This will help you determine how much money you need to cover your needs and objectives, and how much you can save for emergencies or future projects.
To create a list of monthly expenses, start by organizing your information into categories. Consider whether there are any high-cost items that need to be addressed, such as rent or mortgage payments, utility bills, or loan payments.
Next, break down your expenses further by considering other monthly costs. This could include things like groceries, transportation expenses, healthcare costs, insurance premiums, and any other regular payments or bills that occur on a monthly basis.
It’s also important to consider any external stakeholders or funding sources that may impact your budget. For example, if you receive funding from a local agency or organization, you will need to organize your budget to reflect their requirements and any reporting or monitoring needs they may have.
Don’t forget about the in-kind contributions or overhead costs that may be required for certain projects or initiatives. These may include things like office space, equipment, or staff time. Understanding the impact of these costs will help you better allocate your resources.
Once you have an initial list of monthly expenses, it’s important to monitor and track your spending over time. This will help you identify any areas where you may be overspending or where you may have room to cut back. It will also allow you to see how your expenses may change over a given period, such as from month to month or year to year.
Remember, not every expense will be the same every month. For example, you may have additional costs during certain months, such as for holidays or special events. Make a note of these variations so you can plan accordingly.
Finally, it’s important to involve your team or other key stakeholders in the budgeting process. By getting their input and understanding their needs, you can build a budget that aligns with the goals and objectives of your organization or community.
Creating a list of monthly expenses is just one step in the budget planning process. However, it is a critical step that will provide a clear picture of your financial situation and help you make informed decisions about your spending.
Huntington Customer Tip
When it comes to organizing your budget, it’s important to note that every business or organization has different needs and stakeholders. It’s critical to first understand the goals and required expenses of your organization, as well as the level of clarity and information that needs to be provided to stakeholders.
One way to develop a strong budget plan is to think of it as a proposal. Break down your expenses into line-item categories, such as salary, office expenses, and project development. This will help give you a clear understanding of where your money is going and how much is required for each part of your business.
Huntington customers have found success in organizing their budgets by creating a monthly budget plan. This helps them to track their spending and make adjustments as needed throughout the year. It also provides a source of information for stakeholders, such as donors or funding agencies.
When building your budget, consider both fixed and variable expenses. Fixed expenses, such as rent or overheads, are costs that remain the same every month. Variable expenses, on the other hand, can fluctuate based on market prices or the needs of the business.
It’s also important to consider in-kind contributions or donations, as these can help offset some of your expenses. Think about any resources or services that your organization may receive for free or at a reduced cost. By including these contributions in your budget, you can get a clearer picture of your actual expenses.
One common mistake that many organizations make when creating budgets is overlooking external costs. Man-hours or consultant fees, for example, are expenses that may not be immediately obvious but are necessary for project execution. Make sure to account for these costs when creating your budget.
To ensure the success of your budget plan, it’s critical to regularly review and track your performance. This will help you identify any areas where adjustments or reallocations may be necessary. It’s also important to keep an open line of communication with stakeholders to keep them informed of your progress.
Remember, budgeting is an ongoing process. As your business or organization evolves, your budget needs may change as well. Don’t be afraid to make adjustments and revisit your budget as needed.
Period of performance
In developing a budget plan, it is critical to clearly define the period of performance for your project. The period of performance refers to the timeframe in which the project will be executed and the budget will be utilized. This period can vary depending on the nature of the project and the funding source.
For external funding, such as government grants or donations, the period of performance is often specified in the funding proposal. It is important to review the proposal and understand the required performance period before getting started on your budgeting process. If no specific period is mentioned, it is best to assume a standard 12-month period unless otherwise indicated.
Once you know the period of performance, you can start organizing your budget plan accordingly. Begin by listing the specific categories of expenses that your project will require, such as salaries, materials, overheads, or external services. Take into account any ongoing or one-time costs that may arise during the performance period.
When budgeting for salaries, it is important to take into consideration the market rate for the staff you will need. Make sure to include any required benefits or taxes associated with hiring employees. Additionally, consider any potential increases in salaries or changes in staff that may occur during the performance period.
In many cases, budgeting for projects requires a simple monthly breakdown of expenses. This allows for easier tracking and monitoring of spending throughout the performance period. It also helps to develop an emergency savings fund to cover any unexpected costs that may arise. Keep in mind, however, that government funding or other donors may have strict limitations on how much can be allocated for certain expenses.
When developing your budget plan, make sure to clearly identify the source of funding for each expense category. This will help stakeholders and donors understand where their support is going and ensure transparency in your financial management.
A helpful tip when budgeting for projects is to consider in-kind support. In-kind support refers to non-monetary contributions that can help offset project expenses. This could include volunteer work, donated equipment or materials, or free services. Make a note of any anticipated in-kind support you may receive and include it in your budget plan accordingly.
To stay organized and on track, it is important to regularly review your budget plan and make any necessary adjustments. Be flexible and willing to adapt as the needs of your project change. By following these steps and understanding the intricacies of your project’s period of performance, you can develop a strong budget plan that supports your objectives and ensures the successful completion of your project.
How to develop a Budget for your Project Proposal
When developing a budget for your project proposal, it’s important to understand the financial needs and limitations of your organization. You’ll also need to consider the expectations of your stakeholders, whether they be donors, government agencies, or the local community. Here are some key steps to help you create an effective budget:
- Identify your project needs: Before you can start budgeting, you need a clear understanding of what your project will involve. Make a list of the activities, staff, materials, and other resources required.
- Estimate your costs: Break down your project activities and estimate the associated costs. This includes not only direct costs such as staff salaries and materials, but also indirect costs like overheads and administration.
- Understand your funding sources: Determine where your funding will come from and what limitations or preferences these sources may have. Some donors or agencies may only provide funding for specific types of expenses.
- Take a line-item approach: Break down your budget into line items, grouping related expenses together. This makes it easier to track and monitor your spending.
- Consider in-kind contributions: If your project will receive in-kind donations or volunteers, include their value in your budget. This can help demonstrate the full extent of resources being contributed.
- Follow a simple format: It’s important to keep your budget clear and easy to understand. Use a format that allows you to present the information in a logical and organized way.
- Consider an emergency fund: It’s always a good idea to include a contingency or emergency fund in your budget. This can help cover unexpected expenses or changes in circumstances.
- Engage stakeholders: Involve relevant stakeholders in the budgeting process to ensure their buy-in and support. This can help build trust and collaborative relationships.
- Seek external help if needed: If you’re not comfortable developing a budget on your own, consider seeking assistance from finance professionals or organizations that specialize in budgeting.
- Track performance and adjust: Once your project is underway, regularly monitor your actual expenses against your budget. Make adjustments as needed to stay on track.
By following these steps, you can develop a comprehensive budget that aligns with your project proposal and allows you to effectively manage your financial resources. Remember to communicate your budget clearly to stakeholders and make sure it supports the goals and objectives of your project.