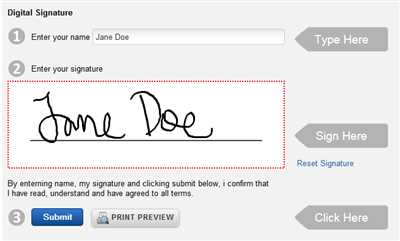
A digital signature is a cryptographic seal used to certify the authenticity and integrity of a digital document or message. It is a process that ensures the identity of the signer and provides a secure way to receive and verify electronic signatures.
When creating a digital signature, users employ various algorithms and processes to generate a unique identifier that is attached to the document or message. This identifier, known as an e-signature, serves as a virtual seal and acts as proof that the document has been signed by its rightful owner.
The process of creating a digital signature typically involves three main steps: hashing, encrypting, and certifying. First, the document is hashed, meaning that it is converted into a fixed-length string of characters. Then, this hash value is encrypted using the signer’s private key, which ensures the integrity and confidentiality of the document.
Once the document is encrypted, it is then certified using the signer’s public key. This key is typically provided by a trusted authority, such as a certificate authority, and serves as a verification mechanism that allows others to validate the authenticity of the signature. Without this certification process, the digital signature would be considered unreliable and potentially invalid.
When recipients of the signed document receive it, they can verify the integrity of the document by performing the process in reverse. This involves decrypting the document using the signer’s public key and comparing the resulting hash value with a newly computed hash value of the received document. If the two values match, it confirms that the document has not been tampered with and provides assurance of its authenticity.
Overall, the creation of digital signatures offers a secure and efficient alternative to traditional signing and postage processes. It eliminates the need for physical documents to be signed and eliminates the wait time associated with sending and receiving signed documents. Furthermore, digital signatures provide a legal basis for electronic transactions, ensuring that the signer’s identity is verified and the content of the document remains intact.
4 Wait for signatures
Once the whole process of creating a digital signature is complete, the documents are generated and sealed using cryptographic processes. The digital signatures and seals add authenticity and integrity to the messages or documents. Users can then wait for the various signers to sign the document, certifying their identity-based e-signatures.
When a signer receives the document for signing, they can review it and sign it using their digital signature. This makes the signature legal and secure, without the need for traditional postage or paper documents.
Typically, the wait for signatures is a simple and cost-effective process. It does not require the physical presence of the signers or any manual intervention. Once all the required signatures are obtained, the document is considered signed and can be used as a legally binding document.
During this process, the authenticity and integrity of the signed document are maintained, ensuring that it cannot be tampered with or modified without detection.
The process of digital signing
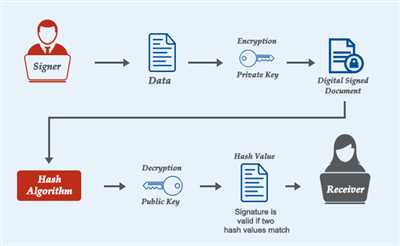
The process of digital signing involves using cryptographic algorithms to create a secure and legally binding signature for electronic documents. This signature ensures the authenticity, integrity, and non-repudiation of the document.
Typically, the digital signing process involves the following steps:
- Identification of the signer: The signer’s identity is verified using various identity-based processes. This may include certifying authorities, biometric identification, or verifying the user’s email address.
- Document preparation: The document that needs to be signed is prepared. This can be done by the sender or by the recipient, depending on the specific e-signature workflow.
- Signature generation: The signer’s digital signature is generated using a cryptographic algorithm. This creates a unique hash value based on the document’s contents.
- Sealing the document: The generated signature is then sealed to the document, ensuring that the document cannot be altered without invalidating the signature.
- Postage and sealing: The signed document is then sent to the recipient through a secure channel. This ensures that the document reaches the intended recipient without any tampering or unauthorized access.
- Receiving and verification: The recipient receives the signed document and verifies its authenticity and integrity. This is done by comparing the received signature with the original signature generated by the signer.
- Legal processes: Once the signature is verified, the signed document can be used for legal purposes. This includes contracts, agreements, or any other legally binding documents.
The whole process of digital signing is simple, cost-effective, and time-efficient. It allows users to sign and receive documents without the need for traditional postage or wait times. With the use of digital signatures, the integrity and authenticity of documents are ensured, making it a secure and reliable method for signing electronic documents.
Using Digital Seals
When it comes to the digital signing process, using digital seals adds an extra layer of security and authenticity to documents. A digital seal is a cryptographic signature that verifies the identity and integrity of a whole document. It is typically used by organizations or individuals who want to ensure the authenticity and integrity of their documents.
Unlike traditional signatures, digital seals use algorithms to create secure signatures that cannot be forged or tampered with. This makes them a more secure and reliable option for signing documents.
The process of using digital seals involves three main steps:
- Generating a digital seal: This is done by using cryptographic processes to create a unique seal that is associated with the identity of the signer.
- Signing the document: Once the seal is generated, it can be used to sign the document electronically. This ensures that the document cannot be altered without invalidating the seal.
- Certifying the seal: After the document is signed, the seal is typically certified to confirm its authenticity. This can be done by using various identity-based processes, such as verifying the signer’s identity or using a trusted certification authority.
Using digital seals has several advantages over traditional signature methods. Firstly, it is a more cost-effective option, as it eliminates the need for postage and physical delivery of documents. Additionally, it is a simpler process that does not require signers to wait for a physical document to be signed and returned.
Furthermore, digital seals provide a higher level of security and integrity compared to traditional signatures. The use of cryptographic algorithms ensures that the seal cannot be forged or tampered with, providing assurance that the document is authentic.
In conclusion, using digital seals is a secure and reliable way to sign documents. It offers the benefits of simplicity, cost-effectiveness, and legal validity. By harnessing the power of digital signatures and cryptographic algorithms, organizations and individuals can ensure the integrity and authenticity of their important documents without compromising on security.