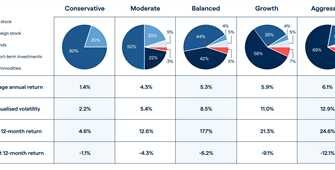
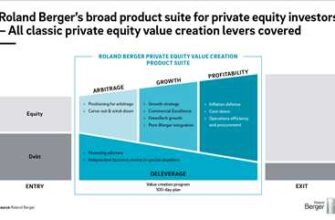
A digital signature is an electronic method of signing a document or message, which is used to authenticate the identity of the signatory and ensure the integrity of the content. Unlike a traditional signature, which is unique to each individual and can be easily forged, a digital signature provides a higher level of security and assurance.
In industries where the verification of identity and authenticity is crucial, such as banking, healthcare, and legal sectors, digital signatures have been widely adopted. They allow signers to securely sign documents without the need for physical presence or scanning of identity documents.
Using a cryptographic infrastructure, a digital signature is created by the signer’s device. It is linked to their unique identity and can only be verified using their private key. Once the signature is verified and the signer’s identity is authenticated, the document or message is considered legally binding.
So, what are the requirements for a digital signature to be considered secure? The digital signature should be unique to the signer and should not be easily replicated or tampered with. It should provide a high level of assurance that the signer is who they claim to be.
Authentication can be done using various methods, such as a username and password, biometric scanning, or even linked to a user’s control device, like a smartphone. Once the signer’s identity is verified, they can digitally sign the document or message and ensure its integrity throughout the communication process.
Understanding Digital Signatures
A digital signature is a cryptographic technique used to verify the authenticity and integrity of digital documents or messages. It provides assurance that a document or message has not been tampered with and that it came from a specific sender or signatory.
When a digital signature is created, it binds a unique cryptographic key to a specific message or document that is being signed. This digital signature is created using the private key of the signer, which is securely stored on their device or in a secure infrastructure. Once the digital signature is generated, it is linked to the signer’s identity and cannot be tampered with.
In order to verify a digital signature, the recipient of the document or message must use the signer’s public key. This public key is used to decrypt the digital signature and check if it matches the original message or document. If the digital signature can be decrypted successfully and matches the message or document, it means that the document has not been tampered with and can be trusted.
Digital signatures are commonly used in various industries and for different purposes. They provide a higher level of authentication and assurance compared to simple scanning or email verification. Digital signatures can be used to sign contracts, authenticate legal documents, ensure data integrity, and much more.
When it comes to digital signatures, it is important to ensure that the signer’s private key is kept securely and that the digital signature is generated using a trusted infrastructure. Without proper control and assurance, digital signatures can be easily forged or manipulated. Therefore, users should be cautious about the sources and requirements for digitally signing documents.
In summary, understanding and verifying digital signatures is crucial in maintaining secure and trustworthy digital communication. By ensuring that a digital signature has been properly linked to the signer’s identity and that the document has not been tampered with, users can have confidence in the authenticity and integrity of digital documents or messages.
What is a digital signature
A digital signature is a unique electronic identifier that is linked with the identity of the signer. It is used in various industries to verify the authenticity and integrity of digital documents. Understanding digital signatures is important for anyone who needs to control and verify the authenticity of documents.
When a signer digitally signs a document, they are using a digital certificate that verifies their identity. This certificate is issued by a trusted third party, such as a certificate authority (CA), and securely stored on the signer’s device.
Once a document has been signed using a digital signature, it can be easily verified by anyone who has access to the signer’s digital certificate. This verification can be done without scanning the actual document or relying on the signer’s email or message to provide assurance of their identity. The digital signature ensures that the document has not been altered or tampered with since it was signed.
To generate a digital signature, the signer uses their private key to encrypt a hash or digest of the document. The encrypted hash is then attached to the document, creating a digital signature. The recipient of the document can use the signer’s public key to decrypt the hash and verify the signature.
A digital signature provides a higher level of assurance than a handwritten signature because it is based on cryptographic techniques. It provides evidence that the document came from the signer and has not been altered since it was signed.
Using digital signatures can simplify the process of signing and verifying documents, as well as provide a higher level of security. They are commonly used in industries such as finance, healthcare, government, and legal to ensure the authenticity and integrity of documents.
With the increasing reliance on digital communication, understanding how digital signatures work and implementing them in your own workflow can help protect your documents and provide an added layer of trust and security.
What about a higher level of identity assurance
In addition to providing a simple way to digitally sign documents, digital signatures can also offer a higher level of identity assurance. This means that the signature can be verified to ensure that the signer is who they claim to be.
At the most basic level, a digital signature is a unique identifier that is linked to a specific user or device. This identifier is created using a combination of the signer’s private key and the contents of the document being signed. Once the signature has been created, it can be securely attached to the document.
To verify the identity of the signatory, the recipient of the digitally signed document can use the signer’s public key to decrypt the signature and compare it with the original document. If the signature is valid, this provides assurance that the document has not been altered since the signature was applied and that the signer is who they claim to be.
In some industries, such as finance or healthcare, a higher level of identity assurance may be necessary. In these cases, additional verification steps can be taken to ensure the signer’s identity. This can include scanning government-issued identification or linking the signature to an authentication service.
With a higher level of identity assurance, the recipient can have more confidence in the authenticity and integrity of the digitally signed document. This can be especially important when dealing with sensitive information or legally binding agreements.
In summary, digital signatures not only provide a simple way to sign documents, but they can also offer a higher level of identity assurance. By understanding the different levels of assurance and utilizing the appropriate verification methods, users can ensure that their signed documents are secure and trusted by the intended recipients.
10 What should I do once my document is digitally signed
Once your document has been digitally signed, there are a few important steps you should take to ensure the security and validity of the signature.
1. Understand the requirements: Familiarize yourself with the legal and industry-specific requirements for digitally signed documents in your jurisdiction. This will help you understand the level of assurance provided by the digital signature.
2. Verify the signature: Use the electronic scanning or verification tools provided by your digital signature infrastructure to ensure that the signature is valid. This will help you confirm the authenticity and integrity of the document.
3. Confirm the identity of the signer: Check the signer’s authentication credentials to verify their identity. This is crucial for ensuring that the signature comes from the intended signatory.
4. Save and archive the document: Store the digitally signed document securely. Make sure to keep a backup for future reference, as well as for compliance with any legal or industry-specific retention requirements.
5. Communicate the signed status: If necessary, inform relevant parties that the document has been digitally signed. This could include sending an email with the signed document attached or using secure messaging systems.
6. Share the document securely: If you need to share the digitally signed document with other parties, ensure that the file is transmitted securely. This can be done using encryption or secure file transfer protocols.
7. Understand the implications: Educate yourself about the legal and practical implications of digitally signed documents in your specific industry. This will ensure that you are aware of any unique considerations or requirements.
8. Use the signature as intended: Consider the purpose of the digital signature and use the document accordingly. For example, a digital signature may be used to provide assurance about the authenticity, integrity, or non-repudiation of the signed message or document.
9. Ensure higher level of assurance if needed: Depending on the sensitivity of the document, you may need to use a higher level of assurance for the digital signature. This can be achieved by using additional authentication factors or advanced signature techniques.
10. Follow up on any related actions: Once the document is digitally signed, make sure to complete any related actions or processes as necessary. This could include notifying other parties, initiating workflows, or updating records.
Источники

When it comes to understanding how a digital signature is done, there are a number of reliable sources that can provide the necessary information. These sources can help you understand the requirements for digitally signing a document, the authentication process, and the level of assurance that comes with a digitally signed document.
One such source is the Electronic Signatures in Global and National Commerce (ESIGN) Act, which provides a legal framework for the use of electronic signatures in various industries. This act outlines the requirements for a digital signature to be considered valid and legally binding.
Another source of information on digital signatures is the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), which has established guidelines for the secure use of digital signatures. NIST provides recommendations on the use of cryptographic techniques and the verification process for digital signatures.
Additionally, organizations like Adobe, which offer digital signature services, provide detailed documentation on how to securely sign a document using their software. These resources can help you understand the process of creating a digital signature and the steps involved in verifying its authenticity.
It is also worth mentioning that some industries, such as healthcare and finance, have specific regulations and guidelines for digitally signing documents. Understanding these industry-specific requirements is important when using digital signatures in these fields.
Overall, by consulting these sources and gaining a better understanding of how digital signatures are done, you can confidently sign documents electronically and ensure the authenticity and integrity of your digital signatures.